ระบบตรวจจับและดับเพลิงในอากาศยาน
Overview
Fire is one of the most dangerous emergencies in aviation. Because an aircraft is a closed environment with limited oxygen and escape options, early fire detection and rapid suppression are vital. Modern aircraft are equipped with multiple systems that continuously monitor and protect critical areas such as engines, cargo compartments, and the cabin.
ไฟเป็นหนึ่งในสถานการณ์ฉุกเฉินที่อันตรายที่สุดในอากาศยาน เนื่องจากเครื่องบินเป็นพื้นที่ปิดที่มีออกซิเจนจำกัดและมีทางหนีจำกัด การตรวจจับไฟไหม้อย่างรวดเร็วและการดับไฟอย่างทันท่วงที จึงเป็นสิ่งสำคัญยิ่ง เครื่องบินสมัยใหม่ถูกติดตั้งด้วยระบบหลากหลายที่ทำงานตรวจสอบและป้องกันไฟในจุดสำคัญ เช่น เครื่องยนต์ ห้องเก็บสัมภาระ และห้องโดยสาร
Fire Detection Systems
Aircraft fire detection systems use sensors that continuously monitor temperature and detect the presence of smoke, heat, or flames. The main types include:
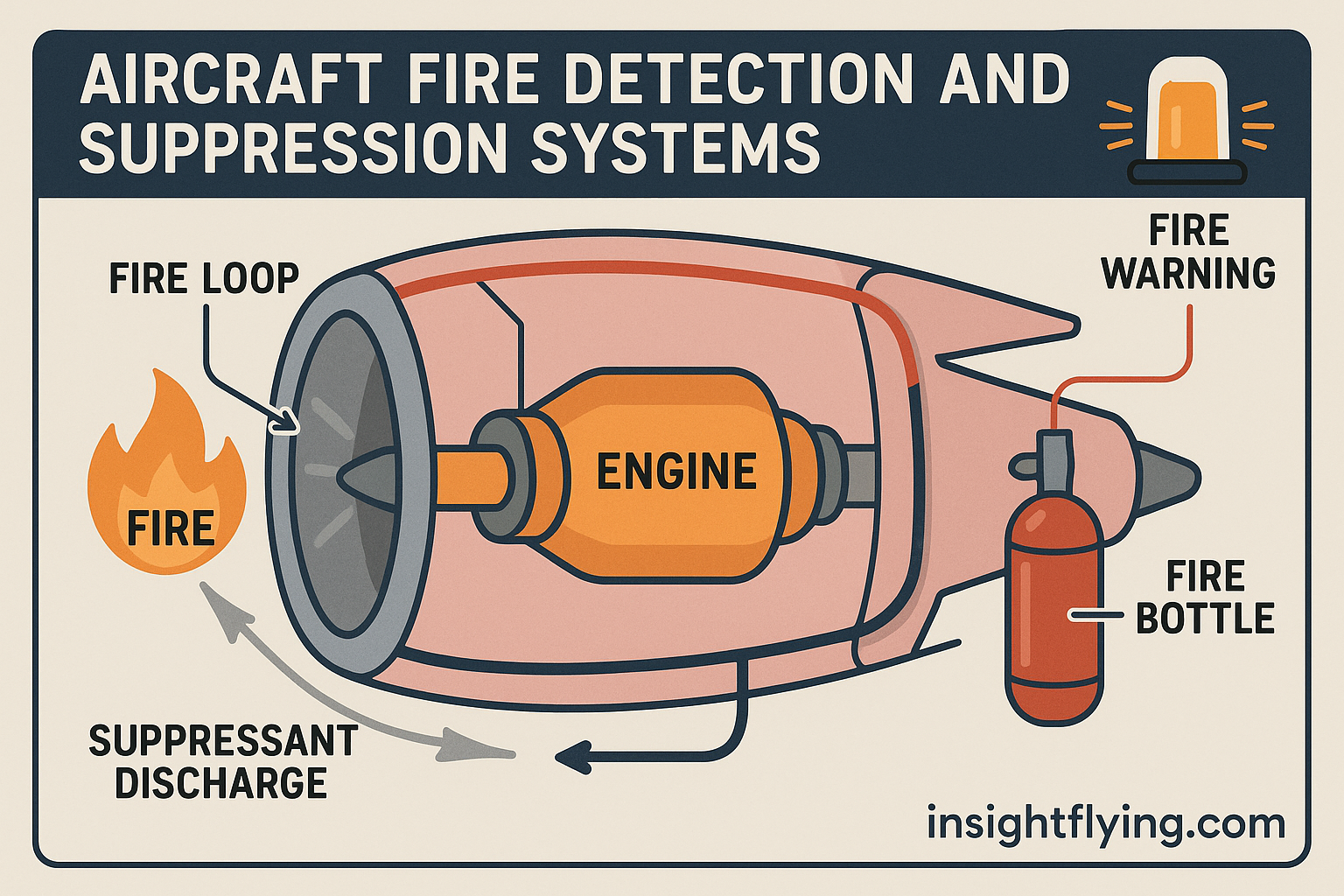
- Continuous Loop Detection Systems – Installed in engines and APU compartments; detect heat along a continuous sensing element.
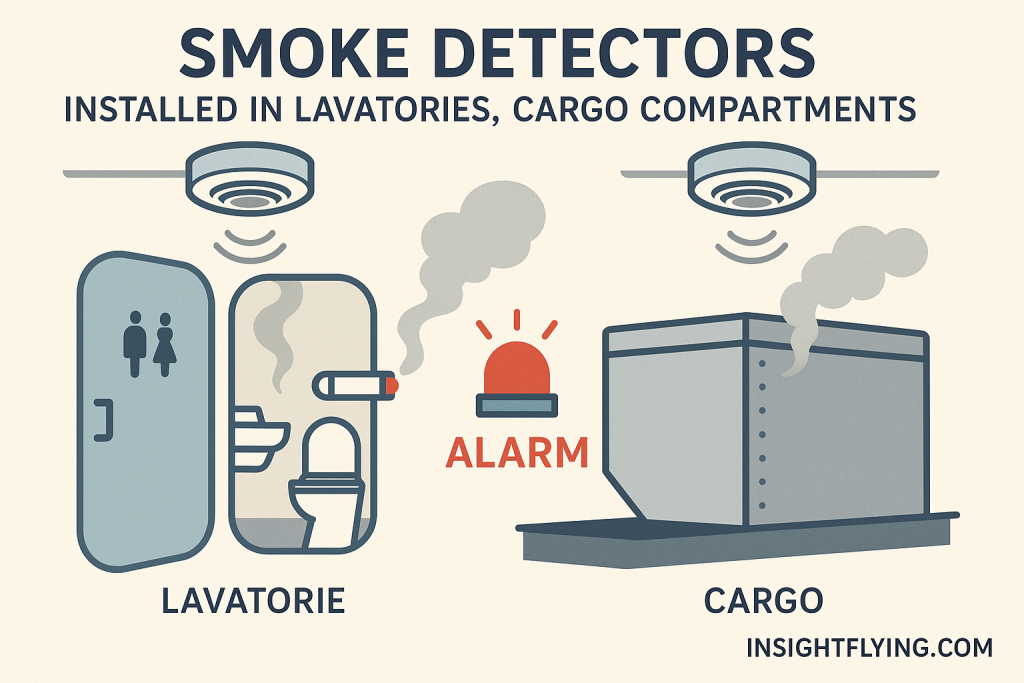
- Smoke Detectors – Installed in lavatories, cargo compartments, and sometimes cabin ceilings; detect smoke particles in the air.
- Temperature Sensors and Overheat Sensors – Monitor specific components such as hydraulic systems or air-conditioning ducts.
ระบบตรวจจับไฟไหม้ของอากาศยานใช้เซนเซอร์เพื่อตรวจสอบอุณหภูมิและตรวจจับควัน ความร้อน หรือเปลวไฟอย่างต่อเนื่อง โดยมีประเภทหลักดังนี้:
- ระบบตรวจจับแบบสายต่อเนื่อง (Continuous Loop Detection) – ติดตั้งในเครื่องยนต์และส่วน APU ตรวจจับความร้อนได้ตลอดแนวของสายเซนเซอร์
- เครื่องตรวจจับควัน (Smoke Detector) – ใช้ในห้องน้ำ ห้องเก็บสัมภาระ และบางครั้งในเพดานห้องโดยสาร เพื่อตรวจจับอนุภาคควันในอากาศ
- เซนเซอร์อุณหภูมิและระบบเตือนความร้อนสูง (Overheat Sensors) – ใช้ตรวจสอบอุณหภูมิในระบบเฉพาะ เช่น ระบบไฮดรอลิกหรือท่อลมปรับอากาศ
Indication and Warning
When a fire or overheat is detected, the system immediately sends a warning to the flight deck. Pilots receive both aural and visual warnings — for example, flashing red “FIRE” lights, a master warning tone, and illuminated fire handles. The system identifies the exact location (e.g., “Engine 1 Fire,” “APU Fire,” “Cargo Smoke”).
เมื่อระบบตรวจจับพบไฟไหม้หรือความร้อนสูงผิดปกติ สัญญาณเตือนจะถูกส่งไปยังห้องนักบินทันที นักบินจะได้รับการเตือนทั้งในรูปแบบ เสียงและแสง เช่น ไฟสีแดง “FIRE” กระพริบ เสียงเตือนหลัก และคันดับเพลิงสว่างขึ้น ระบบยังระบุได้อย่างชัดเจนว่าจุดเกิดเหตุอยู่บริเวณใด เช่น “Engine 1 Fire”, “APU Fire” หรือ “Cargo Smoke”
Fire Suppression Systems
Once a fire warning is confirmed, the pilot or crew can discharge fire extinguishing agents to suppress the fire. Aircraft use different systems for each area:
- Engines and APU: Equipped with Halon bottles connected to discharge lines directed into the fire zones. When the fire handle is pulled and the bottle is discharged, Halon gas floods the area, cutting off oxygen and extinguishing the flames.
- Cargo Compartments: Fitted with smoke detection and automatic suppression systems. Halon or newer eco-friendly agents are released to control the fire and prevent it from spreading.
- Lavatories: Contain automatic extinguishers beneath waste bins, designed to discharge if smoke or heat is detected.
เมื่อได้รับการยืนยันว่ามีไฟไหม้ ลูกเรือสามารถปล่อย สารดับเพลิง (Fire Extinguishing Agent) เพื่อควบคุมไฟได้ โดยแต่ละบริเวณของอากาศยานจะมีระบบที่แตกต่างกัน เช่น
- เครื่องยนต์และ APU: มี ถังสาร Halon เชื่อมต่อกับท่อระบายเข้าสู่พื้นที่เกิดไฟ เมื่อดึงคันดับเพลิงและปล่อยสาร Halon แก๊สจะกระจายปกคลุมพื้นที่ ลดออกซิเจนและดับไฟทันที
- ห้องเก็บสัมภาระ (Cargo Compartment): ติดตั้งระบบ ตรวจจับควันและดับเพลิงอัตโนมัติ โดยปล่อยสาร Halon หรือสารทดแทนที่เป็นมิตรต่อสิ่งแวดล้อมเพื่อควบคุมไฟไม่ให้ลุกลาม
- ห้องน้ำ (Lavatory): มี ถังดับเพลิงอัตโนมัติ ใต้ถังขยะ ซึ่งจะปล่อยสารดับเพลิงทันทีเมื่อมีควันหรือความร้อนสูง
Halon and Alternative Agents
Halon 1301 and Halon 1211 have been widely used for aviation fire suppression because they are highly effective, non-corrosive, and leave no residue. However, due to environmental concerns, the aviation industry is transitioning to Halon alternatives, such as HFC-125, HFC-227ea, and other clean agents that meet fire suppression performance while reducing ozone impact.
สาร Halon 1301 และ Halon 1211 เคยเป็นสารดับเพลิงหลักในอากาศยานเนื่องจากมีประสิทธิภาพสูง ไม่กัดกร่อน และไม่ทิ้งคราบตกค้าง แต่เนื่องจากผลกระทบต่อสิ่งแวดล้อม อุตสาหกรรมการบินจึงเริ่มเปลี่ยนมาใช้ สารทดแทน Halon เช่น HFC-125, HFC-227ea และสารดับเพลิงแบบสะอาดอื่น ๆ ที่ยังคงมีประสิทธิภาพสูงแต่ลดผลกระทบต่อชั้นโอโซน
Crew Response and Training
Cabin and flight crews undergo recurrent training to recognize fire warnings, perform checklist procedures, and fight in-flight fires using portable extinguishers. They are trained to act within seconds — identifying the source, isolating the fire, and using the correct extinguisher type (Halon, water, CO₂) depending on the class of fire.
นักบินและลูกเรือได้รับการฝึกอบรมซ้ำเป็นระยะในการรับมือกับสัญญาณไฟไหม้ ปฏิบัติตามเช็กลิสต์ และดับเพลิงขณะบินโดยใช้ถังดับเพลิงแบบพกพา ลูกเรือต้องสามารถตอบสนองได้ภายในไม่กี่วินาที โดยต้องระบุแหล่งไฟ แยกพื้นที่ และเลือกใช้ชนิดของถังดับเพลิงให้ถูกต้อง เช่น Halon, น้ำ หรือ CO₂ ตามประเภทของไฟไหม้
In Summary
Aircraft fire detection and suppression systems are the unseen guardians of flight safety. They monitor tirelessly, detect instantly, and respond powerfully — giving both crew and passengers the precious time needed to act. Awareness, maintenance, and training keep this invisible shield strong, ensuring that every flight remains safe above the clouds.
ระบบตรวจจับและดับเพลิงในอากาศยานคือ “ผู้พิทักษ์ที่มองไม่เห็น” ของความปลอดภัยการบิน พวกมันทำงานอย่างต่อเนื่อง ตรวจจับได้ทันที และตอบสนองได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ เพื่อมอบเวลาอันมีค่าที่จะช่วยให้ลูกเรือและผู้โดยสารสามารถรับมือได้ทันท่วงที ความรู้ การบำรุงรักษา และการฝึกฝนอย่างสม่ำเสมอ คือสิ่งที่ทำให้เกราะนิรภัยที่มองไม่เห็นนี้คงอยู่ เพื่อให้ทุกเที่ยวบินปลอดภัยเหนือเมฆเสมอ
A320 accident Airbus aircraft airline airmanship attitude aviation Aviation SMS become a captain become a pilot Boeing captain Crisis Crisis Management Dark Aviation Dark Side diversion emergency engine fatigue flight safety go-around Indigo interview judgement management motivation pilot pilot interview qualified pilot safety Safety Management System self-knowledge SMS student pilot technology turbulence weather การจัดการความปลอดภัย การบิน การสอบสัมภาษณ์ นักบิน สอบนักบิน สอบสัมภาษณ์