การทดสอบเครื่องยนต์อากาศยาน — เพื่อความปลอดภัยและความเชื่อถือได้สูงสุด
1. Introduction — The Science Behind Jet Engine Testing
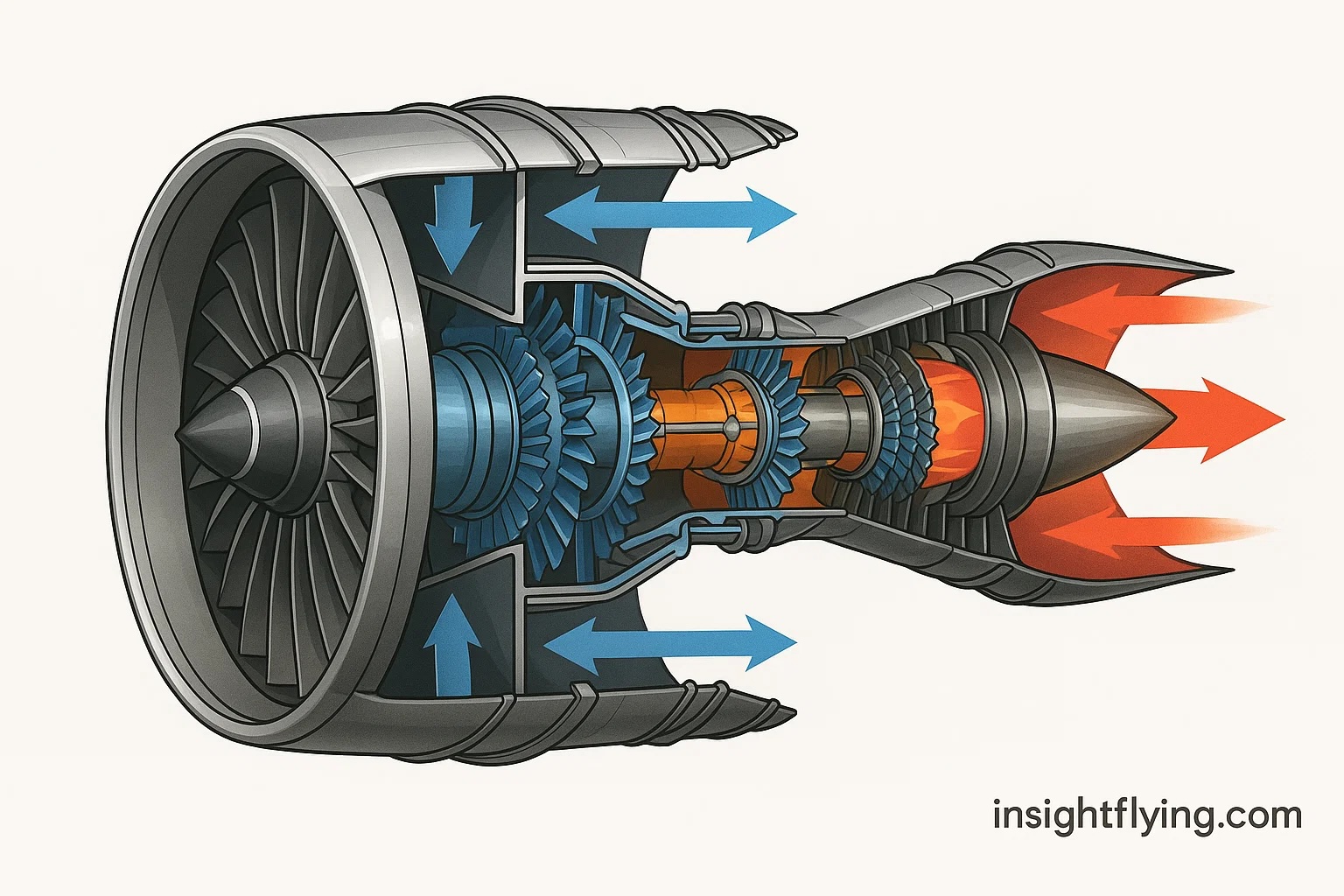
Jet engines are among the most complex machines ever built. They operate at temperatures hotter than molten lava, spin at tens of thousands of revolutions per minute, and must perform flawlessly at 35,000 feet. Engine testing is a vital process that ensures every engine meets strict certification and reliability standards before being installed on an aircraft.
เครื่องยนต์ไอพ่นถือเป็นหนึ่งในเครื่องจักรที่ซับซ้อนที่สุดที่มนุษย์เคยสร้างขึ้น ทำงานที่อุณหภูมิสูงกว่าลาวา หมุนด้วยความเร็วหลายหมื่นรอบต่อนาที และต้องทำงานได้อย่างไร้ข้อผิดพลาดที่ระดับความสูง 35,000 ฟุต ดังนั้น “การทดสอบเครื่องยนต์” จึงเป็นขั้นตอนสำคัญเพื่อรับรองว่าเครื่องยนต์แต่ละลูกมีมาตรฐานความปลอดภัยและความน่าเชื่อถือก่อนติดตั้งกับอากาศยาน
2. What Is Being Tested?
Every engine undergoes a series of performance, structural, and environmental tests. These verify that it can produce rated thrust, resist damage, operate in extreme conditions, and remain controllable at all times.
เครื่องยนต์แต่ละลูกต้องผ่านการทดสอบหลายรูปแบบ ทั้งด้านสมรรถนะ โครงสร้าง และสิ่งแวดล้อม เพื่อยืนยันว่าเครื่องสามารถสร้างแรงขับตามที่ออกแบบ ทนต่อความเสียหาย ทำงานได้ในสภาพสุดโต่ง และควบคุมได้ตลอดเวลา
3. Key Test Categories
3.1 Performance and Endurance Testing
Engines are run for hours or even days to simulate all flight phases: takeoff, climb, cruise, descent, and idle. Sensors record thrust, fuel flow, oil temperature, vibration, and exhaust gas temperature. This verifies performance efficiency and long-term durability.
🔗 Rolls-Royce: How to test a jet engine
การทดสอบสมรรถนะและความทนทานจะจำลองการทำงานของเครื่องยนต์ทุกช่วงการบิน เช่น การขึ้นบิน การไต่ระดับ การบินระดับ และการลงจอด โดยเครื่องยนต์อาจทำงานต่อเนื่องหลายชั่วโมงหรือหลายวัน มีการบันทึกข้อมูลแรงขับ อัตราการใช้เชื้อเพลิง อุณหภูมิน้ำมัน การสั่นสะเทือน และอุณหภูมิไอเสีย เพื่อพิสูจน์ประสิทธิภาพและความทนทานในระยะยาว
3.2 Environmental Testing
Engines face severe conditions: freezing cold at high altitude, scorching heat on the ground, salt from sea air, dust in desert regions, and rain or hail ingestion. Test cells reproduce these environments to check if the engine maintains performance and integrity.
🔗 FAA AC 33.91-1 – Environmental tests
เครื่องยนต์ต้องทนต่อสภาพสุดโต่ง เช่น ความหนาวจัดในระดับสูง ความร้อนสูงบนพื้น ละอองเกลือจากทะเล ฝุ่นทรายในเขตทะเลทราย หรือฝนและลูกเห็บ ห้องทดสอบจำลองสภาวะเหล่านี้เพื่อยืนยันว่าเครื่องยนต์ยังทำงานได้เต็มประสิทธิภาพและโครงสร้างไม่เสียหาย
3.3 Bird Strike and Ingestion Testing
Engines are tested for their ability to withstand the impact of birds or foreign objects. A precisely measured bird carcass or ice block is fired into the engine inlet at operational speed. The goal is not to destroy the engine but to ensure fragments are contained and no catastrophic failure occurs.
🔗 Wikipedia: Blade-off and bird strike testing
การทดสอบการชนของนก (bird strike) หรือการดูดวัตถุแปลกปลอม ใช้เพื่อประเมินความสามารถของเครื่องยนต์ในการทนต่อแรงกระแทก โดยจะยิงซากนกหรือก้อนน้ำแข็งเข้าไปในทางเข้าอากาศของเครื่องยนต์ขณะทำงานจริง จุดประสงค์ไม่ใช่ให้เครื่องพัง แต่เพื่อให้แน่ใจว่าเศษชิ้นส่วนจะถูกเก็บอยู่ภายใน และไม่มีความเสียหายร้ายแรงต่อโครงสร้างหลัก
3.4 Blade-Off Testing
This is one of the most critical safety tests. A fan or turbine blade is intentionally detached during high-speed operation to confirm that the engine casing can contain the fragments and protect the aircraft.
นี่คือการทดสอบด้านความปลอดภัยที่สำคัญที่สุดอย่างหนึ่ง โดยจะจงใจทำให้ใบพัดหรือใบกังหันหลุดออกขณะเครื่องยนต์หมุนด้วยความเร็วสูง เพื่อทดสอบว่าตัวเรือนเครื่องยนต์สามารถกักเศษชิ้นส่วนไว้ได้ และไม่ทะลุออกมาทำอันตรายต่ออากาศยาน
3.5 Noise and Emission Testing
Regulatory agencies like ICAO and FAA require engines to meet limits on noise and exhaust emissions. Testing is done in special acoustic chambers using microphones and exhaust gas analyzers to measure decibel levels and pollutant concentrations.
หน่วยงานกำกับดูแลอย่าง ICAO และ FAA กำหนดข้อจำกัดด้านเสียงและการปล่อยไอเสียของเครื่องยนต์ การทดสอบจะทำในห้องเก็บเสียงพิเศษ โดยใช้ไมโครโฟนและเครื่องวิเคราะห์ก๊าซไอเสียเพื่อวัดระดับเสียง (เดซิเบล) และความเข้มข้นของสารมลพิษ
4. Key Components Under Test
The most critical components include:
- Fan and Compressor Blades – tested for aerodynamic balance and structural fatigue.
- Turbine Blades and Discs – tested under extreme heat to check for creep and oxidation.
- Bearings and Shafts – assessed for vibration and thermal expansion.
- Fuel and Oil Systems – evaluated for flow stability and contamination resistance.
- FADEC System (Full Authority Digital Engine Control) – tested for reliability under lightning, EMI, and vibration.
ส่วนประกอบสำคัญที่ต้องทดสอบ ได้แก่:
- ใบพัดแฟนและคอมเพรสเซอร์ – ตรวจสอบสมดุลอากาศพลศาสตร์และความเมื่อยล้าเชิงโครงสร้าง
- ใบกังหันและจานกังหัน (turbine blades / discs) – ทดสอบภายใต้ความร้อนสูงเพื่อดูการเสียรูปและการเกิดออกไซด์
- แบริ่งและเพลา – ประเมินการสั่นสะเทือนและการขยายตัวเมื่อร้อน
- ระบบเชื้อเพลิงและน้ำมันหล่อลื่น – ตรวจสอบความเสถียรของการไหลและการป้องกันสิ่งปนเปื้อน
- ระบบควบคุม FADEC – ทดสอบความน่าเชื่อถือเมื่อเกิดฟ้าผ่า คลื่นรบกวน และแรงสั่น
5. Case Study: Rolls-Royce Trent 1000 Testing
The Rolls-Royce Trent 1000 engine, used on the Boeing 787, underwent more than 20,000 hours of testing before certification. In a specially built test cell in Derby, the engine endured bird ingestion, fan-blade-off simulation, and high-altitude cold-start tests. Rolls-Royce engineers used over 10,000 sensors to measure every possible parameter — from fuel temperature to shaft speed — ensuring complete understanding before entering service.
🔗 Rolls-Royce Trent 1000 testing story
เครื่องยนต์ Trent 1000 ของ Rolls-Royce ซึ่งใช้กับ Boeing 787 ผ่านการทดสอบมากกว่า 20,000 ชั่วโมงก่อนรับรอง ในการทดสอบที่ศูนย์ Derby มีการจำลองเหตุการณ์การดูดนก การแตกของใบพัด และการสตาร์ตเครื่องที่อุณหภูมิหนาวจัดระดับสูง วิศวกร Rolls-Royce ติดตั้งเซนเซอร์กว่า 10,000 จุดเพื่อวัดทุกพารามิเตอร์ ตั้งแต่อุณหภูมิน้ำมันเชื้อเพลิงจนถึงความเร็วเพลา เพื่อให้มั่นใจว่าเครื่องยนต์พร้อมใช้งานอย่างสมบูรณ์
6. Importance for Airlines and Maintenance
Reliable engines mean fewer in-flight shutdowns, lower maintenance costs, and better fuel economy. Airlines benefit from reduced downtime, while passengers enjoy safer and quieter flights. Engine testing also helps engineers predict maintenance intervals, plan overhauls, and introduce performance upgrades.
เครื่องยนต์ที่ผ่านการทดสอบอย่างเข้มงวดจะช่วยลดความเสี่ยงการดับกลางอากาศ ลดต้นทุนซ่อมบำรุง และเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพเชื้อเพลิง สายการบินจึงมีเวลาใช้งานมากขึ้น ผู้โดยสารก็ได้รับความปลอดภัยและความเงียบสบายระหว่างบิน นอกจากนี้ ข้อมูลจากการทดสอบยังช่วยให้วิศวกรคาดการณ์รอบการซ่อมใหญ่ วางแผนการบำรุงรักษา และปรับปรุงสมรรถนะได้ต่อเนื่อง
7. Reference Links & Further Reading
- FAA Advisory Circular AC 33.91-1 – Engine Component Tests
- Rolls-Royce – How to test a jet engine
- MTU Aero Engines – Inside an Engine Test Cell
- EDF Inc. – Science Behind Jet Engine Testing
- Wikipedia – Blade-off and Containment Testing
A320 accident Airbus aircraft airline airmanship attitude aviation Aviation SMS become a captain become a pilot Boeing captain Crisis Crisis Management Dark Aviation Dark Side diversion emergency engine fatigue flight safety go-around Indigo interview judgement management motivation pilot pilot interview qualified pilot safety Safety Management System self-knowledge SMS student pilot technology turbulence weather การจัดการความปลอดภัย การบิน การสอบสัมภาษณ์ นักบิน สอบนักบิน สอบสัมภาษณ์